How a Lab Grown Diamond Detector Identifies Synthetic Diamonds
Discover how a lab grown diamond detector works to spot synthetic diamonds with precision. Learn the key features that make detection accurate and reliable.
Lab grown diamonds, also known as synthetic diamonds, have become increasingly popular due to their affordability and ethical production methods. In fact, the global market value of lab grown diamonds reached over $27.2 billion in 2023.
However, distinguishing these from natural diamonds can be challenging, as both share identical physical properties. This is where lab grown diamond detectors come into play. These advanced diamond detection machines utilize technologies such as UV light analysis and electrical conductivity tests to accurately identify synthetic stones.
For jewelers and consumers alike, understanding how these diamond testers function is crucial in ensuring the authenticity of their gemstones.
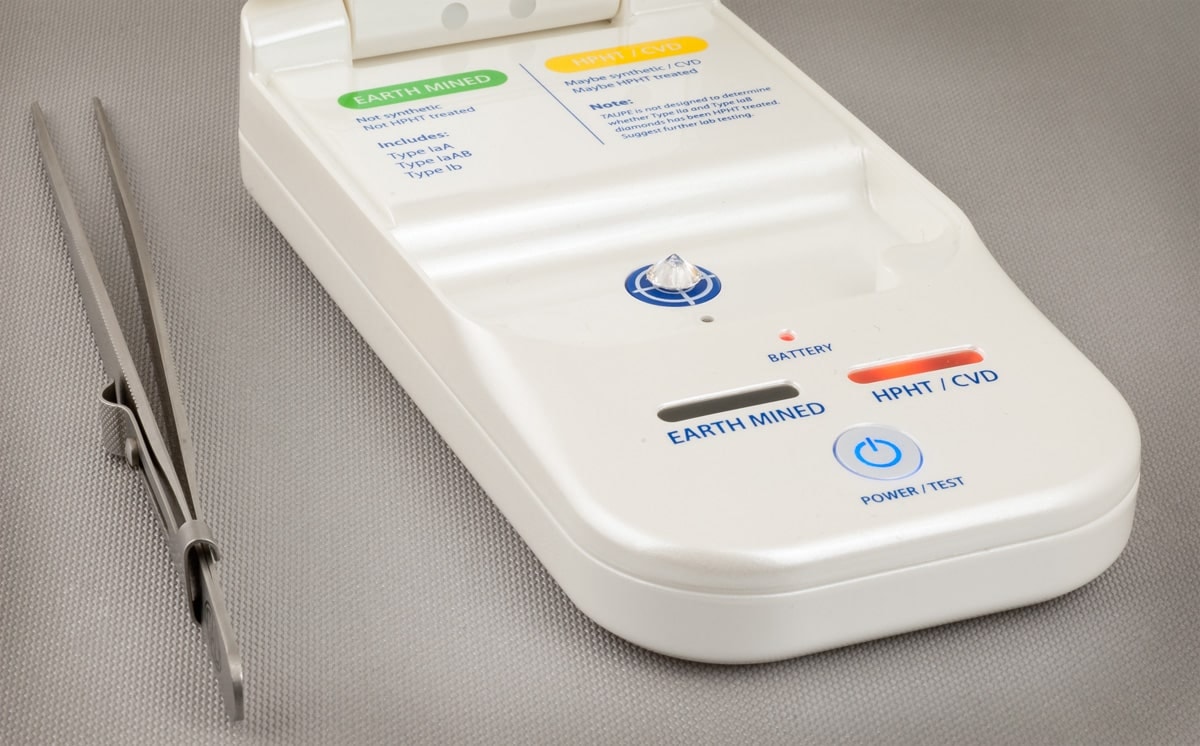
What Is a Lab Grown Diamond Detector?
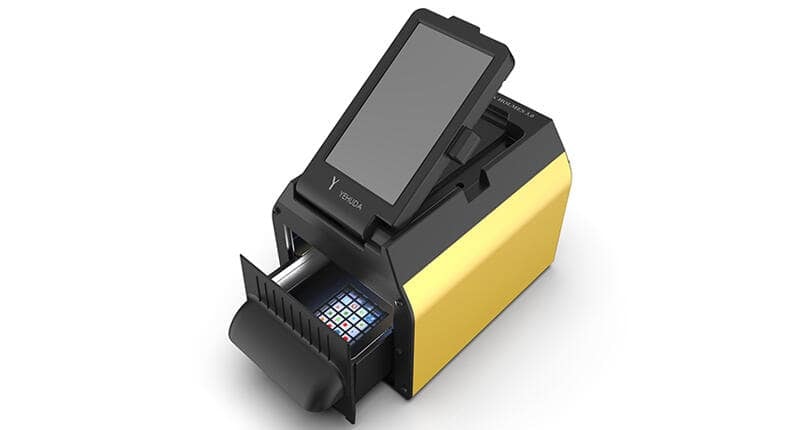

A lab grown diamond detector is a screening equipment designed to determine if a diamond is created in a lab or mined naturally. It helps jewelers, manufacturers, and customers avoid mistakes when verifying authenticity. These technologies use advanced methods to check features like inclusions, fluorescence, and structure, making them essential for the jewelry industry.
How Does It Work?

-
The process starts by analyzing the diamond’s material properties using advanced technology.
-
It checks for signs of moissanite, cubic zirconia, and diamond simulants to rule out fake stones.
-
Special equipment detects type IIA diamonds, which are often lab created.
-
Real diamonds and lab alternatives show differences in growth patterns, which the detector examines.
-
Jewelers use this solution to verify stones before selling to clients.
-
Research ensures accuracy, reducing errors in manufacturers' testing.
-
These tools are widely used in the business of engagement rings, rings, and jewelry to maintain quality and trust.
How Do Diamond Detection Machines Accurately Identify Lab Grown Diamonds?

Diamond detection machines utilize advanced technology to distinguish between natural and lab-grown diamonds. For instance, De Beers Group Ignite's AMSMicro device can screen approximately 2,200 diamonds per hour, efficiently identifying lab-grown stones.
These machines often employ Raman spectroscopy, which detects subtle differences in crystal structures, aiding in accurate identification.
Additionally, devices like the iD100 use photoluminescence spectroscopy to differentiate diamonds based on their unique spectral signatures.
By leveraging these innovative techniques, the jewelry industry can effectively identify lab-grown diamonds, ensuring transparency and maintaining consumer trust.
What do Diamond Testers Check for?
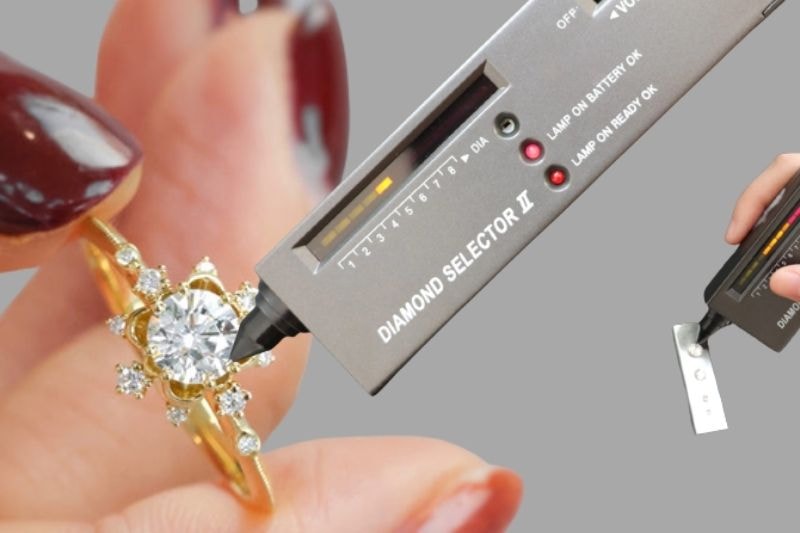

1. Thermal Conductivity
-
Diamond testers use heat sensors to detect lab grown diamonds by measuring how quickly they transfer heat.
-
Innovation in testing devices has improved accuracy, making it easier to distinguish between stones.
2. Electrical Conductivity
-
Natural and lab grown diamonds conduct electricity differently, which helps in identification.
-
Some example tests measure conductivity variations to rule out simulants.
3. UV Light Response
-
UV light helps identify fluorescence patterns, a key factor in testing.
-
GIA research has shown that different diamonds react uniquely under UV exposure.
4. Fluorescence Patterns
-
Fluorescence can vary between natural and synthetic stones.
-
Advanced testers analyze fluorescence at the forefront of detection methods.
5. Refractive Index
-
The way light bends in a diamond helps determine if it is real.
-
The majority of mined diamonds have a refractive index of 2.42, whereas other stones differ.
6. Hardness and Durability
-
Diamond testers check hardness using scratch tests.
-
A dedication to precision ensures no mistake in results.
7. Response to High-Frequency Waves
-
High-frequency waves detect density variations.
-
Modern service tools are designed to identify inconsistencies in structure.
What are the Common Detection Challenges?

1. Hidden Inclusions
-
Some lab grown diamonds have inclusions that mimic natural ones, making detection difficult.
-
Advanced innovation in detection tools helps spot these microscopic details.
2. Inaccurate Handheld Testers
-
Some handheld devices fail to identify subtle differences in diamonds.
-
GIA studies show that more precise screening methods are needed for accurate results.
3. HPHT & CVD Similarities
-
Detecting lab grown diamonds made through HPHT and CVD is challenging due to similar growth structures.
-
Many service providers use spectroscopic analysis to overcome these detection issues.
4. Unstable Growth Patterns
-
Lab grown diamonds often have inconsistent growth, unlike natural stones.
-
The majority of synthetic diamonds display unique growth patterns under magnification.
5. Post-Growth Treatment Issues
-
Some diamonds undergo treatments that alter their properties.
-
Dedication to research helps improve detection of these modifications.
6. Mounted Diamond Testing Limits
-
When diamonds are set in jewelry, detection becomes harder.
-
Some tools struggle with stones placed in store settings, requiring specialized screening.
7. Lack of Standardized Methods
-
No universal guideline exists for team members conducting tests.
-
The mission of gemological organizations is to develop standardized, reliable testing procedures.
How Do Natural Diamonds Differ from Lab Grown Ones?

-
Natural diamonds take millions of years to form deep within the earth, whereas lab grown diamonds are produced in controlled settings within weeks.
-
Mined diamonds often contain unique inclusions, while lab grown ones have more uniform structures.
-
Advanced technologies help identify the subtle differences in crystal growth patterns and chemical composition.
Mined Diamond vs. Lab Grown: Which Needs More Testing?
-
Mined diamonds usually undergo fewer tests since their natural origin provides certain identifying features.
-
Lab grown diamonds require more testing due to their controlled process and lack of natural formation markers.
-
Screening for quality in synthetic diamonds involves checking for growth inconsistencies.
-
Jewelers use advanced equipment to differentiate between natural and synthetic stones.
-
Both types need verification, but synthetic ones demand stricter screening to confirm authenticity.
-
The difference in formation affects how each stone reacts to light and heat tests.
-
Some clients prefer mined diamonds due to their natural history, while others choose lab-grown options for ethical reasons.
Conclusion
Identifying diamonds isn’t as simple as it seems, especially with how advanced synthetic options have become. A lab grown diamond detector helps jewelers, buyers, and researchers make informed decisions with confidence. As detection methods continue to evolve, accurate testing ensures clarity in the market.
Whether you're purchasing a stone or verifying authenticity, using the right tools makes all the difference. Understanding these technologies helps avoid confusion and ensures every diamond gets the validation it deserves. If you're working with diamonds, investing in reliable testing solutions is always a smart move. After all, knowing what you have is what truly matters.














